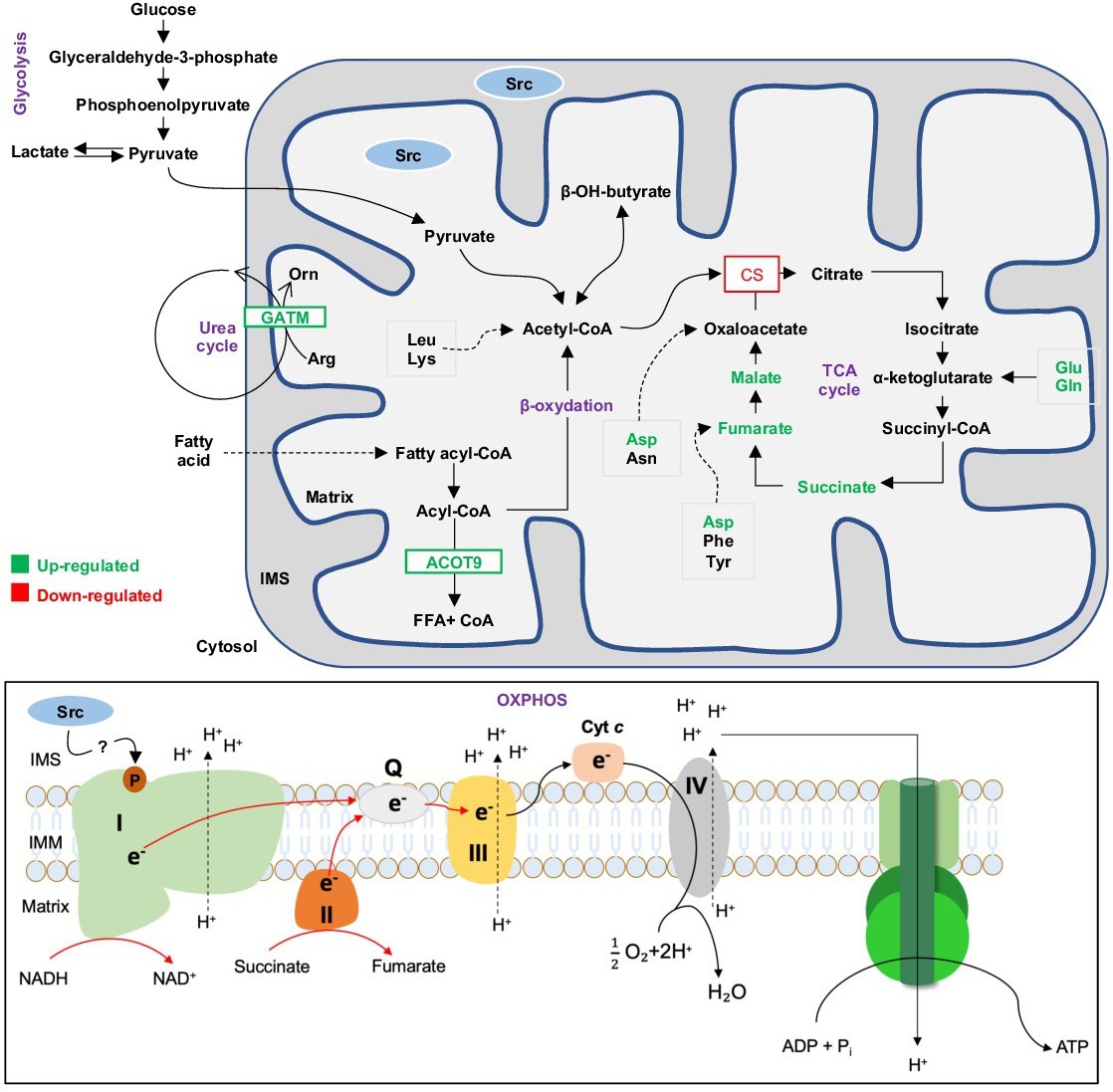
Fig. 6. Deletion of Src induces shifts in hepatic metabolism. Representation of metabolic alterations observed in liver of Src-/- mice. Major metabolic pathways are indicated (in purple): glycolysis, urea cycle, β-oxydation, tricarboxylic (TCA) cycle and oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS). Oxidation of amino acids are also indicated. Previous works suggested that Src is present in IMS whereas our findings indicate that Src is also localized in the matrix. Deletion of Src increased levels of proteins GTAM (glycine amidinotransferase) and Acyl-CoA thioesterase 9 (ACOT9), amino acids aspartate (Asp), glutamate (Glu), glutamine (Gln) and of TCA cyle intermediates malate, fumarate and succinate (indicated in green) in liver of mice fed ad libitum. These changes were associated with lower activities of citrate synthase (CS), and of electron transport system complexes I, II and III (indicated by red arrows) in liver of Src-/- mice fed ad libitum. Phosphotyrosine proteomic analyses showed lower levels of phosphorylated NDUFA8 in liver of Src-/- mice fed ad libitum, suggesting that Src target (directly or indirectly) this CI subunit. Arg: Arginine; Asn: Asparagine; Asp: Aspartate; Cyt c: Cytochrome c; e-: electron; Gln: glutamine; Glu: glutamate; FFA: Free Fratty Acid; IMM: Inner Mitochondrial Membrane; IMS: Intermembrane Space; Leu: Leucine; Lys: Lysine; Orn: Ornithine; Phe: Phenylalanine; Q: Ubiquinone; Tyr: Tyrosine.